How to add secret files to Vets-API
Last Updated: October 27, 2025
vets-api uses AWS SSM Parameter Store to store secrets and other variables that may be necessary for services to function properly such as for Settings. This guide provides details and best practices for storing and using secret files.
Overview of steps
Acquire a secret file
Create an AWS Parameter Store parameter
Add Parameter to
secret.ymlfiles for vets-apiAccess the file via the secret directory and file name
The following sections will provide more detail on what, where, and how to use a secret file in vets-api and roughly correspond to steps 2-4.
What is a secret file
Secret files are keys, certs, tokens, or any other file that shouldn’t be shared or stored in the codebase. These files are typically .key, .crt, or .pem files. For example, let’s say you need to use a .key to authenticate with an external api.
Where to store the secret file
All secrets files are stored in the dsva-vagov/<service-name>/<ENV>/<file_name> path in the Parameter Store.
All shared team secrets (secrets that belong to a team and not to a service) will be in a top-level path leading with the team name, e.g.: cms, devops, frontend-team. The team who creates a path will have full permission to edit any secret in that path.
Here’s an example parameter: dsva-vagov/vets-api/dev/my_fake_service_key. Certs and keys need a trailing newline at the end of the value.
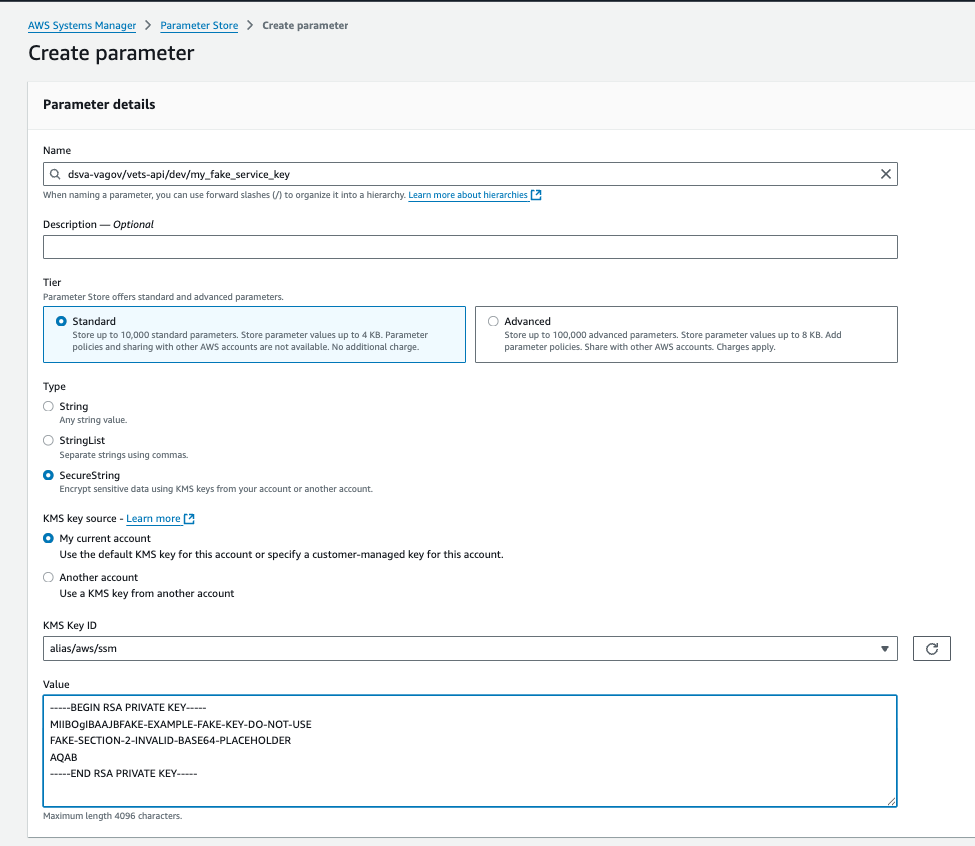
Adding a secret file to Param Store
How to use the secret file
vsp-infra-application-manifests
Add your new secret file to the app-secret-dir definition of secrets.yaml file in the vsp-infra-application-manifests repo. Make sure the name is unique. Otherwise the file might get overwritten by another secret entry.
---
apiVersion: "kubernetes-client.io/v1"
kind: ExternalSecret
metadata:
name: app-secret-dir
namespace: {{ .Release.Namespace }}
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/hook: PreSync
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: "-3"
spec:
backendType: systemManager
data:
# add your secret to the bottom of the list
- key: /dsva-vagov/vets-api/dev/my_fake_service_key
name: my_fake_service_key.keyHere’s a link to the staging secrets.yaml for vets-api: https://github.com/department-of-veterans-affairs/vsp-infra-application-manifests/blob/main/apps/vets-api/staging/templates/secrets.yaml
dev has two app-secret-dir for the new and old EKS cluster. You must add them to both.
It’s a good practice to name your secret file the same name (in the above case my_fake_service_key.key) in each environment. This will allow you to hardcode the value in settings.yml and skip an additional Param Store Parameter.
vets-api
The app-secret-dir is mounted at /srv/vets-api/secret, so to access your key in vets-api you’ll need to use the above path and your file name.
For example, you can access your file via settings.yml like this:
my_fake_service:
auth:
secret_key_path: "/srv/vets-api/secret/my_fake_service_key.key"Here’s an example implementation of the key with Settings:
# /srv/vets-api/secret/my_fake_service_key.key
key_path = Settings.my_fake_service.auth.secret_key_path
key_file = File.read(key_path)
private_key = OpenSSL::PKey::RSA.new(key_file)Troubleshooting
Key not found
There is likely a mismatch in the Parameter path, ExternalSecret definition (app-secret-dir), or settings value
If the issue is in dev (live not local) only then double-check that you’ve added the key to both the new and old EKS cluster in secrets.yaml
Key not parsable
If the key is found but not parsable, the key data may be malformed or invalid. Review the Parameter value.
Rails server failed to deploy/boot
If the server failed to deploy/boot especially if the failure is in db-migrate, it’s likely an issue in the settings.yml file. Review the spacing (or tabs) of the newly added setting and ensure the Parameter value has a trailing new line.
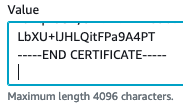
See trailing extra line
Help and feedback
Get help from the Platform Support Team in Slack.
Submit a feature idea to the Platform.
